-
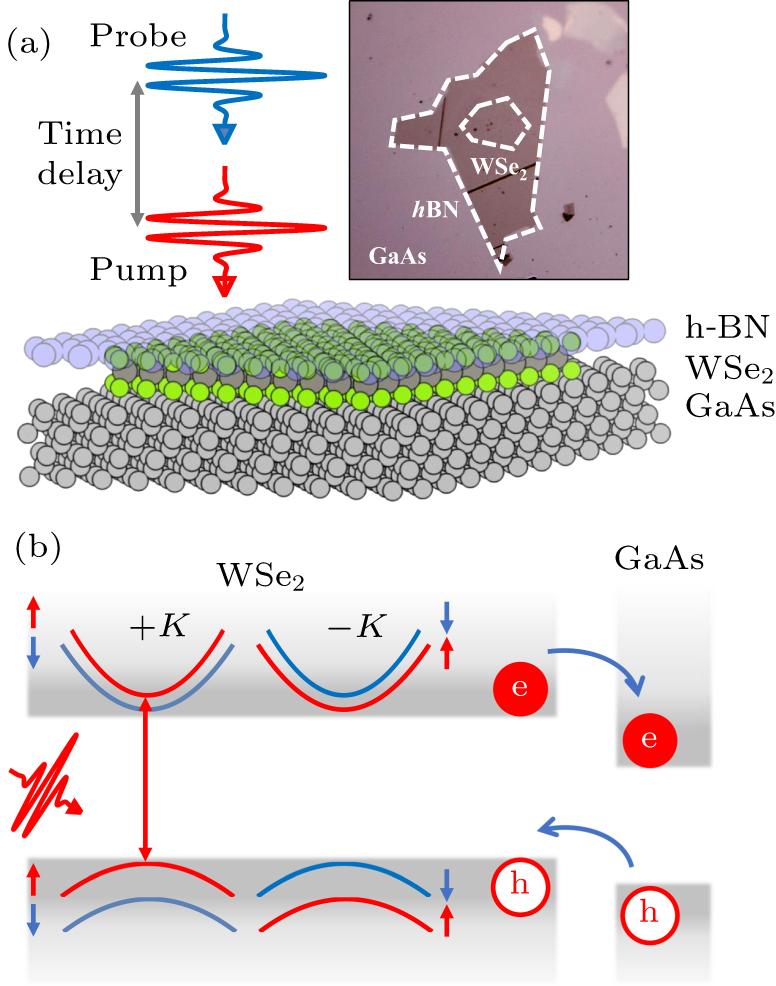
Figure 1. (a) Schematic structure and an optical microscopy image of the prepared WSe2/GaAs heterostructure protected by h-BN flake. (b) Band alignment and schematic charge transfer process in WSe2/GaAs heterostructure upon optical excitation.
-
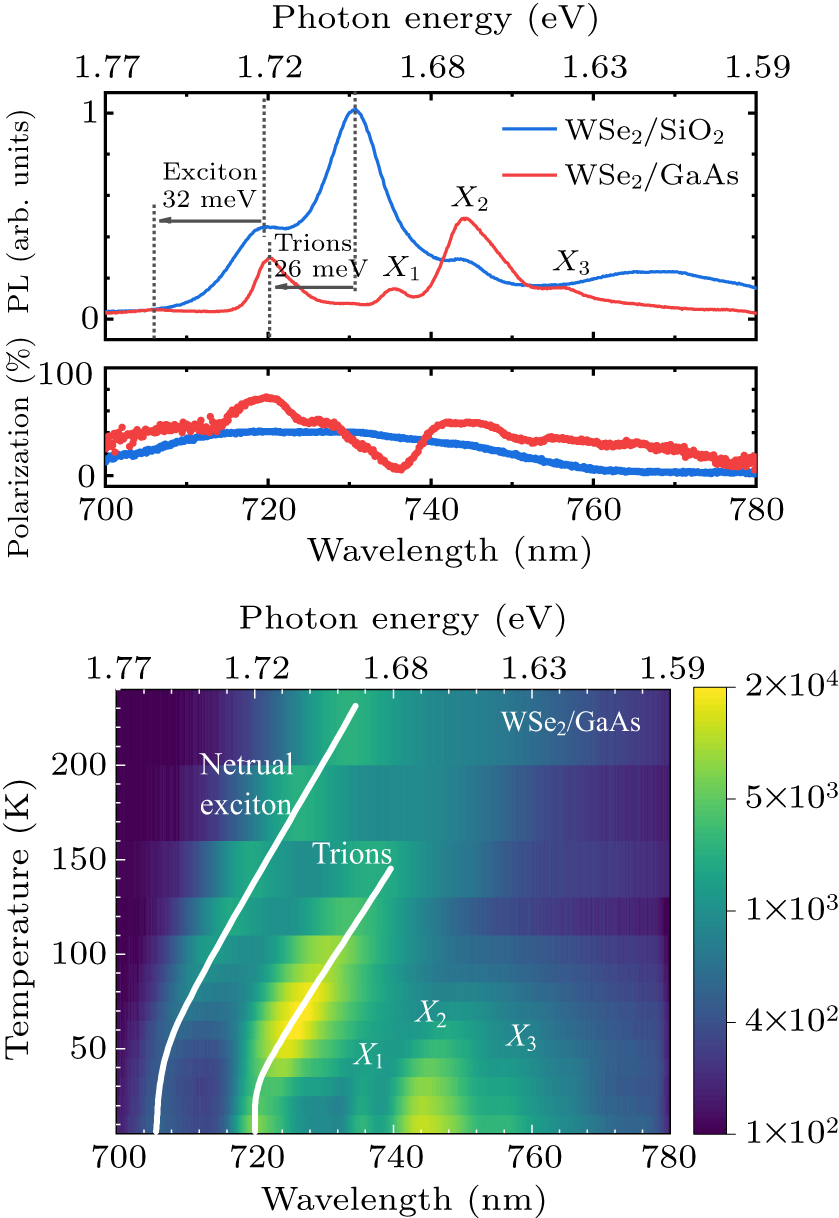
Figure 2. (a) PL spectra of the WSe2/GaAs and WSe2/SiO2 (upper panel), as well as the deduced circular polarization degree (lower panel) for both samples measured at temperature of 10 K. (b) Temperature-dependent PL intensity contour plot of WSe2/GaAs (logarithmic coordinate).
-
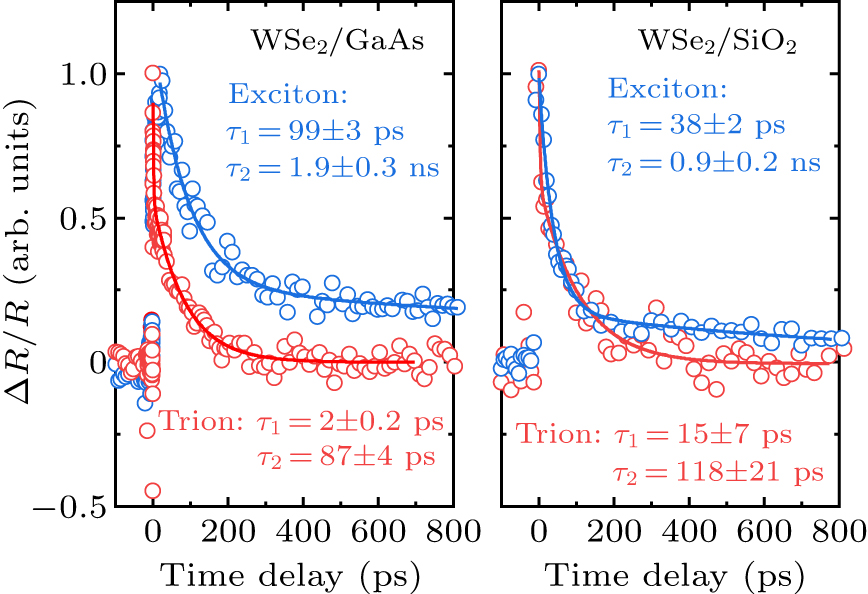
Figure 3. The degenerate TRR (ΔR/R) results of the two samples with the pump and probe photon energies tuned to be resonant with those of neutral exciton and trions for both samples. Dots represent experimental data, and lines are fitting results.
-
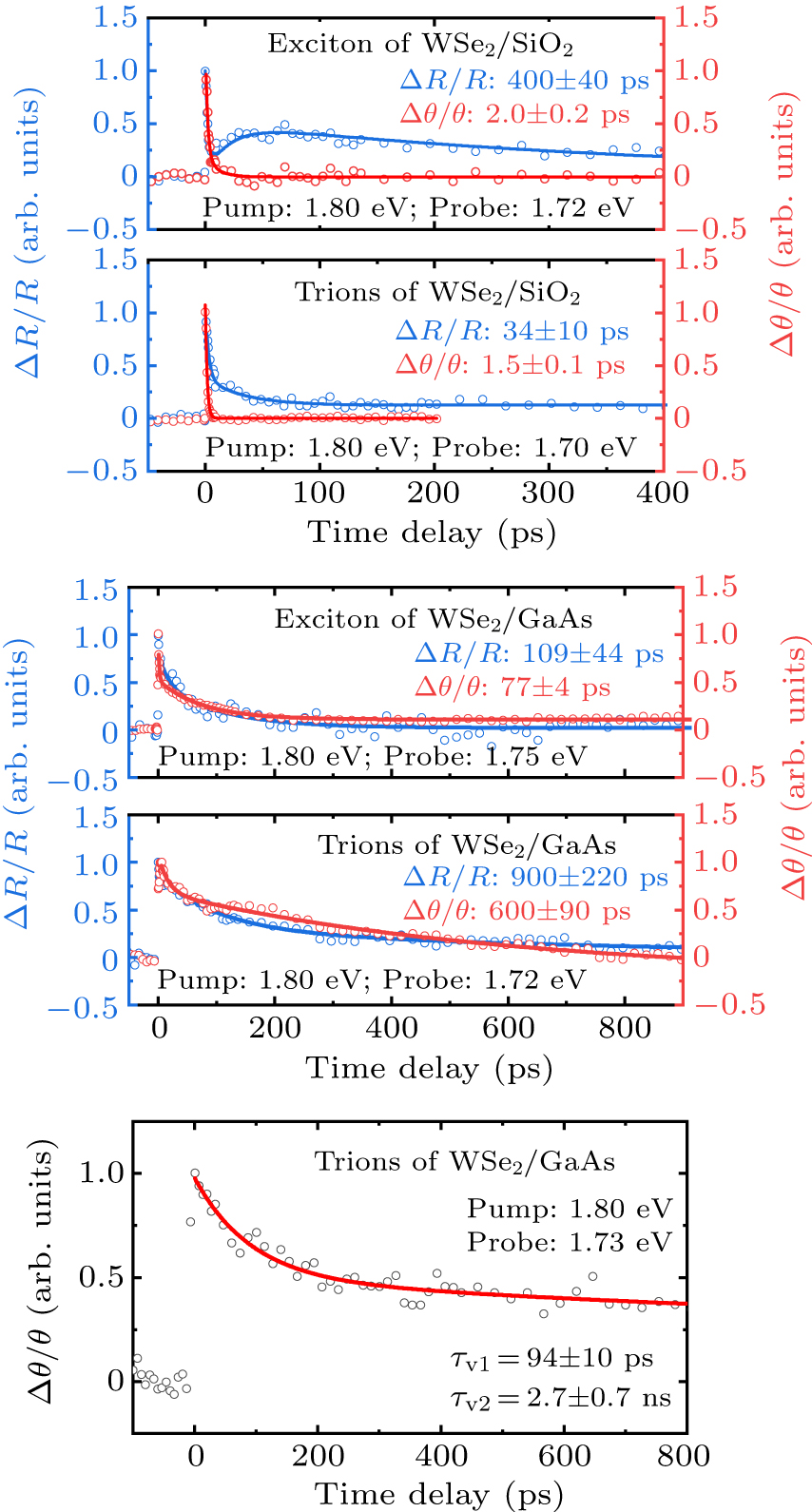
Figure 4. The TRR and TRKR results measured with pump photon energy of 1.80 eV, and probe photon energy tuned to be resonant with the exciton and trions for (a) WSe2/SiO2 and (b) WSe2/GaAs. Lifetimes noted in (a), (b) are long-lived components extracted from the bi-exponential fittings. It is seen that the valley polarization of trions in WSe2/GaAs survives two orders of magnitude longer than that in WSe2/SiO2. (c) TRKR results under pumping at 1.80 eV and fine tuning probe at 1.73 eV for the trions in WSe2/GaAs.
-
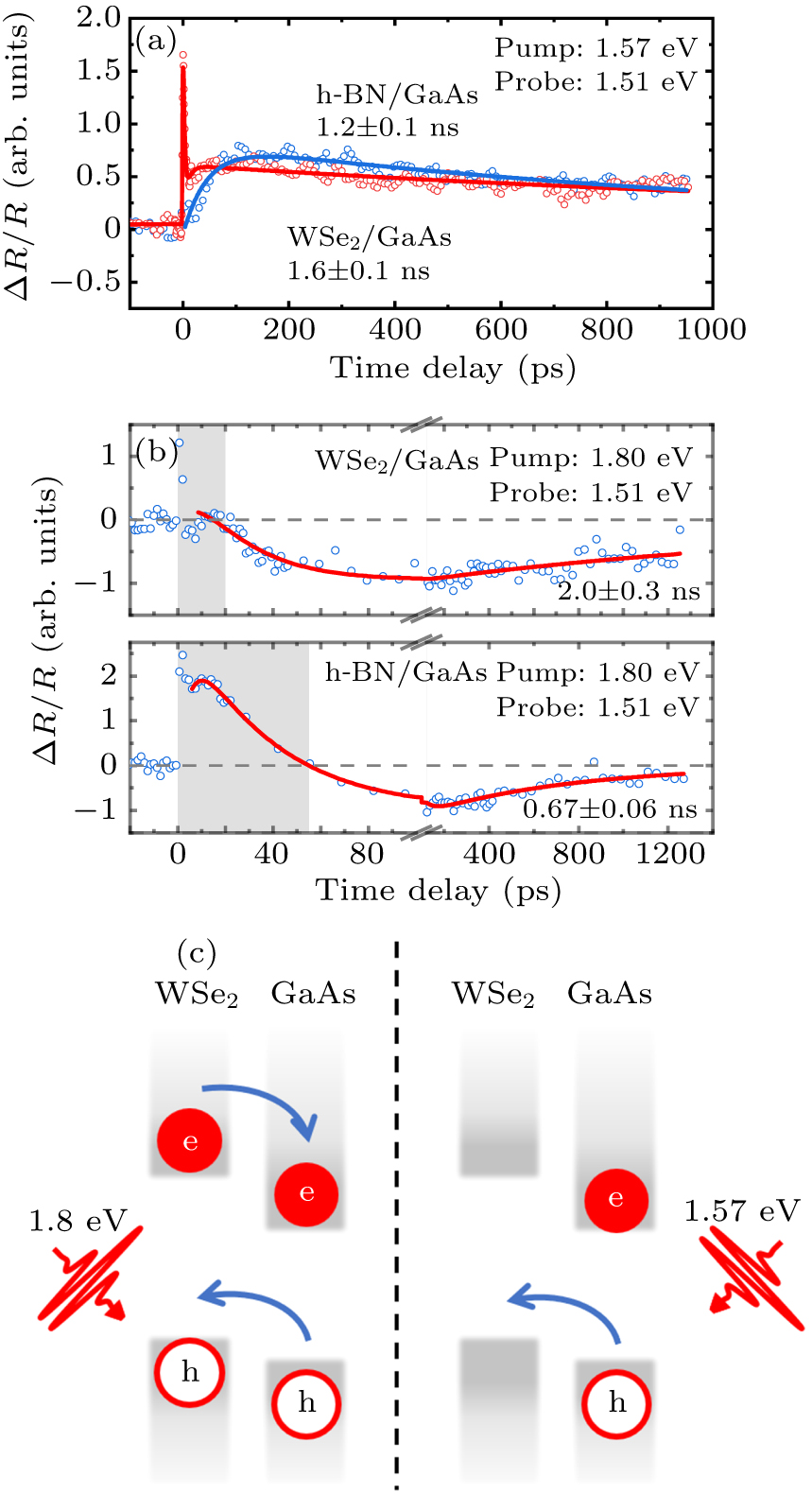
Figure 5. The ΔR/R measurements at 10 K for the carrier dynamics of GaAs in both the WSe2/GaAs heterostructure and GaAs wafer. Here, the probe photon energy was fixed to be in resonance with the bandgap of GaAs at 10 K (1.514 eV). (a) The ΔR/R results measured at pump photon energy of 1.57 eV, at which only GaAs can be optically excited. The excited holes in GaAs transfer to WSe2, resulting in the reduced band renormalization of GaAs. (b) The ΔR/R results measured at pump photon energy of 1.80 eV. Both GaAs and WSe2 can be optically excited, so that electrons in WSe2 can participate in the transfer process, giving rise to significant band renormalization of GaAs. (c) Schematic diagram of charge transfer process under different excitation conditions.
Figure
5 ,Table
0 个